Do you often wake up exhausted after a full night’s sleep? Do you snore loudly? Wake up in the middle of the night gasping for air? Sleep disorders are a surprisingly prevalent yet often overlooked health concern, concealing their impact as silent conditions. If you answered “yes” to the questions above, don’t panic, but it’s possible that you may suffer from sleep apnea. Yet most people are unaware that they have any medical conditions related to sleep and usually blame it on circumstances or external factors. The key to getting good quality sleep every night is to identify common risk factors and symptoms to reduce the possibility of having a sleep disorder — such as sleep apnea. Of course, if you suspect a serious condition, you should always “test, not guess” and seek advice from a qualified medical authority.
Sleep is essential for our well-being so what happens when we can’t breathe properly during sleep? In this article, we’ll delve into the risk factors leading to sleep apnea, its symptoms, and existing treatments.
Sleep Apnea Overview: Types & Effects
Sleep apnea is a silent condition affecting an estimated 26% of adults between the ages of 30 and 70. It’s also estimated that as many as 80% of apnea cases go undiagnosed. But what exactly is it? How does it affect you? Do you have it? We hope to provide answers to these questions in this article.
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder in which a person’s breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. It happens when the muscles in the back of the throat fail to keep the airway open, resulting in partial or complete obstruction of airflow. As the body struggles to resume normal breathing, this can lead to loud snoring, gasping, or choking sounds.
These breathing interruptions can last anywhere from a few seconds to more than a minute and can occur repeatedly during the night. Based on its causes, the way it manifests, and its symptoms, there are two types of sleep apnea: Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) and Central Sleep Apnea (CSA).
-
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
OSA is the most common type of sleep apnea in which the muscles in the back of the throat fail to keep the airway open while sleeping. This causes breathing pauses that can last several seconds or longer, causing a person to wake up gasping for air. Studies reveal that 10% of adult Americans have a mild form of the disorder, while 7.5% deal with moderate or severe obstructive sleep apnea.
Obstructive sleep apnea is characterized by loud snoring and excessive daytime sleepiness, and it is usually linked to obesity, smoking, alcohol consumption, and a genetic proneness to the condition.
-
Central Sleep Apnea
CSA is a less common form of sleeping disorder that affects more men over 60 than others. Unlike OSA, central sleep apnea is not caused by a physical obstruction in the airway, but rather by brain failure to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. CSA is frequently linked to underlying medical conditions like heart failure, stroke, or neurological disorders. Breathing difficulties and pauses, as well as unreasonable daytime sleepiness, are all symptoms of central sleep apnea.
5 Signs You May Have Sleep Apnea
Several warning signs occur when you suffer from sleep apnea. Even though the most common symptom of sleep apnea is loud, chronic snoring, not everyone who snores has apnea. Let’s take a look at these other signs noticed among people with sleep apnea.
- Waking up gasping for air: If you frequently wake up choking or gasping for air, this obstruction of airflow is a clue that you may have sleep apnea.
- Daytime drowsiness and fatigue: Improper rest caused by sleeping disorders might make you feel sleepier than usual during the day interfering with your usual activities and making you fall asleep at unusual times.
- Trouble concentrating: Trouble falling asleep and constantly waking up during the night prevents you from getting quality sleep that can lead to problems with concentration and memory during the day.
- Waking up with a dry mouth: If you wake up with a dry mouth, it could be due to an obstruction from sleep apnea that causes you to breathe through your mouth.
- Waking up with a sore throat or hoarse voice: Extreme dryness of your throat muscles is caused by excessive snoring, frequently linked to sleep apnea.
Most Common Causes of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea can have several underlying causes and it is usually linked to unhealthy habits, age, genetics, or severe medical conditions. Depending on the type of apnea you have, here are some things that can cause breathing sleep disruptions.
Risk factors of obstructive sleep apnea include:
- Enlarged tonsils or adenoids can obstruct the airway and make it difficult to breathe during sleep.
- Age — As you get older, fatty tissue in your neck and tongue can accumulate, increasing your risk of sleep apnea.
- Obesity — Excess weight can put pressure on the airway, making it more likely to block up during sleep.
- Lifestyle habits such as smoking or drinking alcohol. Smoking causes inflammation which obstructs the airflow and leads to heart disease or heavy breathing. Alcohol, on the other hand, makes your throat relax, causing your upper airway to close.
When it comes to central sleep apnea, there are other causes at play, as it is linked to your brain and heart functions. CSA is linked to:
- Medical conditions such as heart failure, high blood pressure, strokes, or neurological disorders, disrupt the brain’s ability to control breathing.
- Medications such as opioids or sedatives, can suppress breathing and contribute to CSA.
Breathing Problems Affect Your Body and Mind
We all know that not getting enough sleep can lead to several health problems, so the earlier you identify any sleeping conditions, the better!
When it comes to sleep apnea, the first effect after you wake up is an intense headache, especially due to low blood oxygen. Moreover, an immediate effect of fragmented sleep is experiencing daytime fatigue and difficulty concentrating. You may feel tired and lethargic during the day and experience lower productivity levels. In the long run, if left untreated, sleep apnea can worsen existing health conditions.
Sleep is tightly linked to a good mental state, so any sleep disorders cause an increased risk of depression and anxiety, as well as memory loss issues. Moreover, sleep apnea can cause spikes in blood pressure during sleep, which can lead to hypertension over time. High blood pressure can increase the risk of heart disease, strokes, coronary artery disease, atrial fibrillation, and heart failure. Learn more about the connection between sleep and heart health.
Often, sleep apnea patients also report having Type 2 diabetes, which contributes to insulin resistance and poor glucose control, increases the risk of nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision problems. Lastly, poor sleep quality can also disrupt hormones that regulate hunger and metabolism, making it challenging to maintain a healthy weight. But perhaps the most alarming of all are the serious health risks. Individuals with moderate to severe sleep apnea have a much higher risk of mortality, stroke, and cancer.

Sleep Apnea and Health Risks. Individuals with moderate to severe sleep apnea showed a significantly higher risk of Mortality, Stroke, and Cancer over 20 years. Source: https://www.clearvuehealth.com/b/sleep-apnea-dangers/
Treatments for Sleep Apnea
Overall, sleep apnea can have a significant impact on both physical and mental health. It is essential to seek treatment to reduce the risk of health problems and improve quality of life. If you have a severe case, seek the advice of a qualified medical provider because there are proven treatments depending on the severity and type you have. Medical treatments may include:
- Some patients may require surgery;
- Medication for the condition.
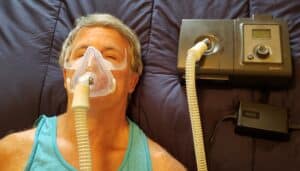
- Commonly, a CPAP machine, which delivers a continuous stream of air to keep the airway open, is recommended for apnea sufferers.
- Oral appliances and positional therapy devices can also be effective for mild to moderate cases. Find an experienced dentist to be fitted correctly.
A Few Tips for Healthier Sleep
On the bright side, there are a few habits you can include in your sleeping routine to reduce the risk of sleep apnea or relieve its symptoms.
- Establish a consistent sleep schedule. Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate your body’s sleep-wake cycle and improves sleep quality.
- Create a healthy bedtime routine. Avoiding caffeine and nicotine before bedtime, limiting screen time before bed, and engaging in relaxing activities before bed can all help improve sleep quality.
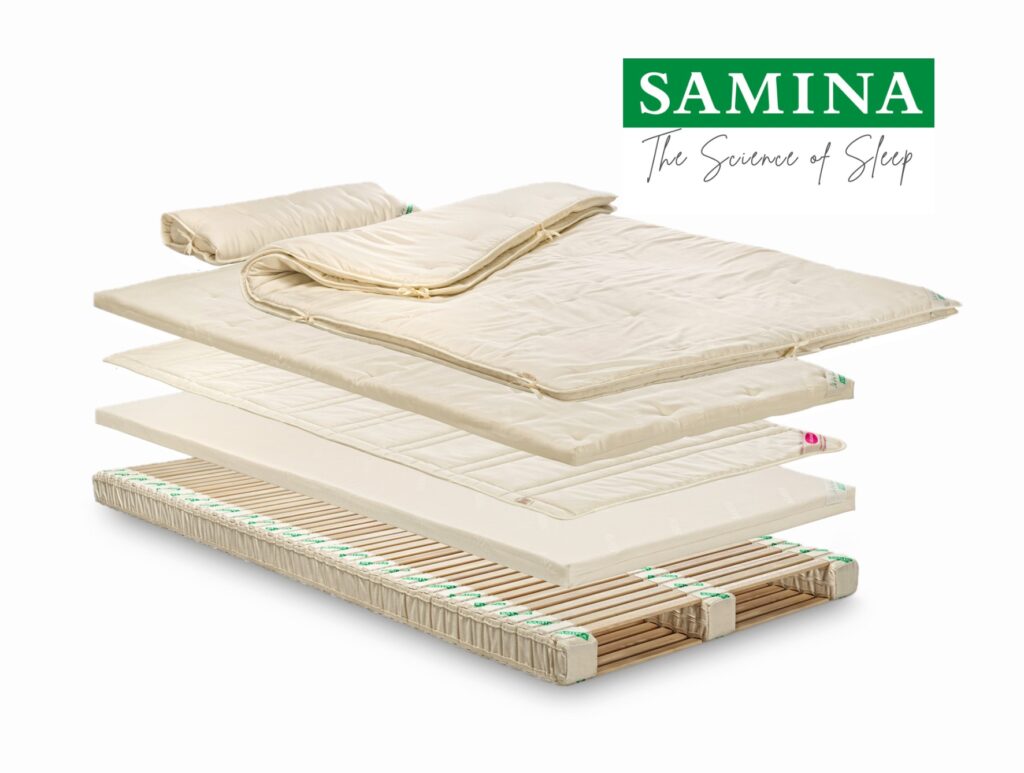
- Additionally, the right mattress to support your healthy sleep like a SAMINA healthy sleep system can help lessen pressure points for a comfortable sleeping position and reduce snoring.
- Consider inclined sleeping. An inclined bed has a lot of benefits for your body, as it reduces mouth breathing therefore limiting the symptoms of sleep apnea to promote restorative breathing.
- Swap your old pillow contaminated with bacteria from drool and filled with dust mites for a new orthopedic pillow that will help you breathe better with the right support for your neck and head.
- Be sure your bedding and mattress toppers are nontoxic and natural for the healthiest sleeping environment.
Elevate Your Sleeping Experience with Samina!
Sleep disorders can take a toll on your overall health and well-being. SAMINA Sleep is bringing the earthy feeling of sleep directly into your home, offering a range of products that promote healthy sleep. From natural rubber mattresses, inclined bed frames, and accessories — SAMINA is here to help you elevate your sleep! If you wonder what it even feels like to be well-rested, we need to talk.
So why wait? Contact SAMINA today to find out more about the right sleep system for you!